Choosing high-quality steel structure components determines safety, service life, and total project cost. Engineers must evaluate material grade, section accuracy, fabrication quality, and protection systems. Each factor influences load capacity, fatigue resistance, and maintenance needs.
Global steel consumption in construction exceeds 1.8 billion tons annually, according to World Steel Association data. Structural steel failures often link to poor component selection rather than design errors. Poor component selection often increases lifecycle costs by over 20 percent. Good selection reduces structural risk and improves construction efficiency.
Material grade of steel structure components
Material grade forms the foundation of component quality. Different countries and regions have different standards for steel grades. For example, Q235 and Q355 are commonly used in structural steel in China. In the United States, ASTM A36 and ASTM A572 Grade 50 are commonly used. EN S355 components are the most common in the European market.
With the development of business globalization, there will be more and more cross-border purchases. In order to solve the problem of different product and raw material grade standards. Suppliers are required to provide authoritative material certificates to ensure that the yield strength, tensile strength and elongation of their products meet the standards of the purchaser. The yield strength of Q235 steel is not less than 235Mpa, and Q355 steel is similar to EN S355, reaching 355MPa. The yield strength of ASTM A36 is not less than 250Mpa, and ASTM A572 Grade 50de is about 345Mpa.
Cross-section size and geometric accuracy of steel structure components
The cross-section size is the core parameter that determines the carrying capacity, tensile strength and stiffness of the component. Taking hot-rolled H-shaped steel as an example, when the height is less than 400mm, the allowable deviation of the flange width is generally controlled within ±2mm, and the deviation of the web thickness should not exceed ±0.5mm. The straightness of the component is also critical, and the deviation is usually not greater than 1/1000 of the length of the component. For example, for a 12-meter-long beam, the bending deviation should be less than 12mm.
The geometric accuracy of the components will affect the carrying efficiency and installation difficulty of the components. Steel structure buildings have extremely high requirements for installation accuracy during construction. The accuracy error of the component in the size or mounting hole will cause the component to fail to be installed smoothly as designed. This not only requires the construction party to carry out on-site modification of the components, increasing the project time and cost, but also accumulates risks and increases the safety risks of the building.
It becomes necessary to choose a larger supplier. Because large and high-quality suppliers generally have ultrasonic testing machines, laser cutting machines, 3D CNC drilling and other equipment. These equipment can reduce the accuracy error of components in welding and machining. The cutting size error can be controlled within ±1mm, and the drilling position error does not exceed ±0.5mm.At the same time, large suppliers generally have a team of experienced designers, which can avoid many risks and troubles in advance.
Anti-corrosion treatment of steel structure components
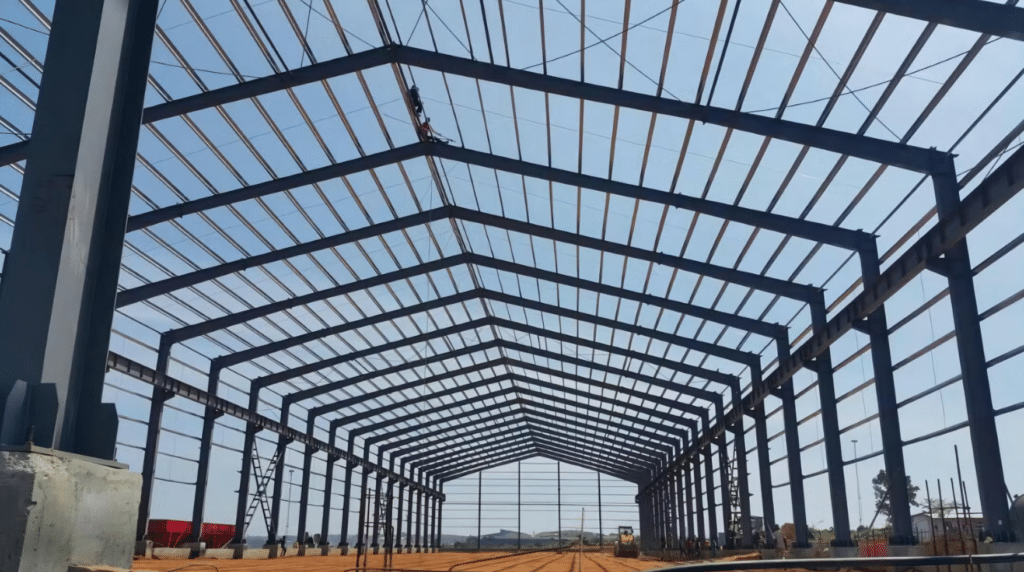

In view of the easy rust of steel products, anti-corrosion treatment is an important part of measuring the service life and quality of steel structure components.Generally, the anti-corrosion treatment of steel structure components is divided into three links, namely anti-rust coating, shot blasting and rust removal, and anti-rust coating.
Hot-dip galvanized is a common protection method for steel.The thickness of the zinc layer is generally 65 to 85µm, which can provide protection for more than 30 years in a moderately corrosive environment.This link is usually provided directly by the steel raw material manufacturer.After the production is completed, the manufacturer needs to blast the components.Through the continuous impact of high-speed rotating shot blasting, the dirt and rust on the surface of the components are peeled off.At the same time, this process will increase the roughness of the surface of the component and enhance the adhesion of the coating.

Paint spraying is the last step in the anti-rust treatment of steel structures. Workers will use different coatings to spray the components multiple times.High-quality coating systems are usually composed of multiple layers such as epoxy primer, intermediate paint and polyurethane topcoat, with a total thickness of 200µm.This system ensures the protection of the surface of the component by the coating to the greatest extent, and can ensure an anticorrosive cycle of 15-20 years.
Connection components that cannot be ignored
Connection components often govern structural reliability. Bolts, plates, and anchors must match load demands. High-strength bolts usually follow ASTM A325 or A490 standards. ASTM A325 bolts provide minimum tensile strength of 830 MPa. A490 bolts reach 1,040 MPa. Use slip-critical connections for dynamic loads. These connections require surface friction coefficients above 0.35. Pretension forces for M20 A325 bolts reach about 172 kN.
Connection plates should match or exceed the parent steel grade. Plate thickness typically ranges from 8 to 25 mm in industrial buildings. Anchor bolts must resist both tension and shear. Grade 8.8 anchor bolts provide yield strength of 640 MPa. Proper edge distance prevents concrete breakout. Minimum edge distance should equal at least four bolt diameters. Accurate component selection at connections reduces joint failure risk by over 40 percent in extreme events.







Leave A Comment